Your Doctor can readily assess your glucose levels by blood-analysis, however there are also many diagnostic tests which can be carried out in your home which are very effective in finding out the degree of onset for diabetes.
Type 2, or adult onset diabetes, is a metabolic disorder that results when the body cannot make enough or properly use insulin, a hormone that converts food to energy.
This differs from type 1 diabetes, in which people must take daily insulin shots because their bodies don’t produce any insulin, and is most commonly diagnosed in children and young adults.
According to the American Diabetes Association, type 2 diabetes accounts for 90 to 95 percent of diabetes cases.
The number of people with diabetes has doubled in the past decade, with the ever-mounting and enormous strain upon global health care funding. It is one of the most preventable diseases facing developed nations, yet every year the incidence of diagnoses increases.
In the United States Alone, approximately 10% of the population have diabetes with millions of new cases annually.
Finnish researchers found that diet and exercise counseling resulted in a 58% reduction in diabetesrisk among people who are prime candidates for developing the condition, which is associated with obesity and sedentary lifestyle.
The Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP), a trial published in 2002, found intensive lifestyle interventions such as diet or exercise were more effective than the diabetes drug metformin in preventing the onset of type 2 diabetes.
Self-Diagnosis
One fairly accurate method of assessing the amount of glucose in the urine is Benedict’s test. It can be done safely in your home for less than $10.
It is essential that the test be performed two hours after a meal. In the initial stages of the disease, a diabetic does not lose sugar in his urine, when on empty stomach. Hence if the Benedict’s test is performed in the fasting state, it is possible to miss the diagnosis of the disease.
Benedict’s reagent is a chemical reagent commonly used to detect presence of reducing sugar(s), however other reducing substances also give a positive reaction. This includes all monosaccharides and many disaccharides, including lactose and maltose.
The principle of Benedict’s test is that when reducing sugars are heated in the presence of an alkali, they get converted to powerful reducing compounds known as enediols.
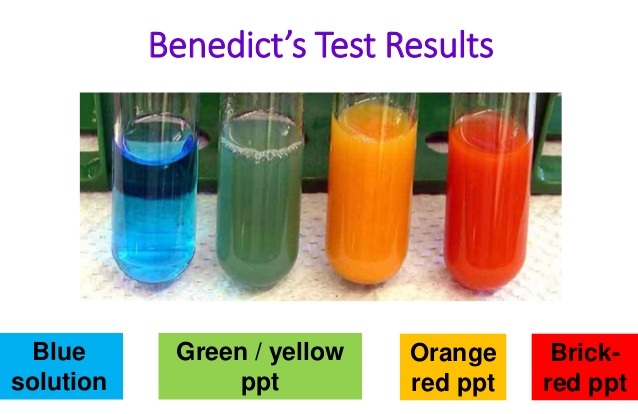
The color of the obtained precipitate gives an idea about the quantity of sugar present in the solution, hence the test is semi-quantitative.
If it remains blue, there is no concentration of sugar in the solution. A greenish precipitate indicates about 0.5 g% concentration; yellow precipitate indicates 1 g% concentration; orange indicates 1.5 g% and brick red indicates 2 g% or higher concentration.
Benedict’s Solution can be obtained from Amazon, as well as many other online and local retailers and pharmacies.
Apparatus:
- Benedict’s solution (fresh; not more than 3 months old),
- Dropper,
- Test-tube and test-tube holder
Procedure:
Take 5 ml (one teaspoon) of Benedict’s solution in the test-tube. Holding the test-tube with the holder, heat it over a spirit lamp till the Benedict’s Solution boils without overflowing. The test-tube can also be placed in boiling water.
Drop 8 to 10 drops of urine into the boiling Benedict’s solution. After again boiling the mixture, let it cool down. While cooling, the mixture changes colour.
Please note:
- The Benedict’s test is not a definitive test for glucose. It is an aldehyde test. Hence, it will give coloration even if other sugars are present in the urine, such as maltose, galactose, fructose, sucrose, etc.
- Some antibiotics can give positive results due to presence of aldehyde groups in them. Examples are aspirin, penicillin and vitamin C antibiotics.
- The Benedict’s test shows results only when the blood sugar is increased by more than 180mg%. Hence, mild cases of diabetes mellitus cannot be confirmed.
By April McCarthy, Prevent Disease